Communication is essential—a universal truth. In the wilderness, where cell signals fade, staying connected becomes more challenging. While many venture into nature to escape modern communication, safety often requires a way to handle emergencies or bad decisions. Others may need regular contact with the outside world for personal or professional reasons.
That's where satellite messengers, personal locator beacons, and other backcountry communication devices come in. We're here to help you navigate these options. Our guide will take you step by step through selecting the right device to match your needs and preferences.
Types of Wilderness Communication
Below, we discuss products and services that contact the outside world, without cell signal, from the wild. We further limit our discussion to those devices and systems that provide digital, text-based communication. Voice transmission (as provided by satellite phones, two-way radios, and walkie talkies) is, paradoxically, less clear, more expensive, and complicated to execute. Sometimes, of course, it is the best choice. Here, we are discussing text-based communication. Some devices and services provide voice-only or all that a texting product does and more. Anything that includes voice is significantly more expensive and at least a little bulkier than the average text-only product. You don't need voice contact for human-powered, recreational, terrestrial wilderness adventures. If you do, you likely have connections and contacts to help you choose.
Emergency Messaging
The simplest and arguably most important type of communication is the SOS message. Sending a message that contains your location, as deduced by GPS triangulation, and alerts a dispatcher to your need for help is the most common and least expensive sort of backcountry communication. An SOS message like this, regardless of which system it employs, conveys nothing more than your location and that you need help. This is, therefore, suitable only for “life or limb” emergencies. Transmitting more nuanced information about the nature of your emergency with an SOS message is impossible. Some devices, predominantly those using the COSPAS/SARSAT network, only perform SOS messaging.
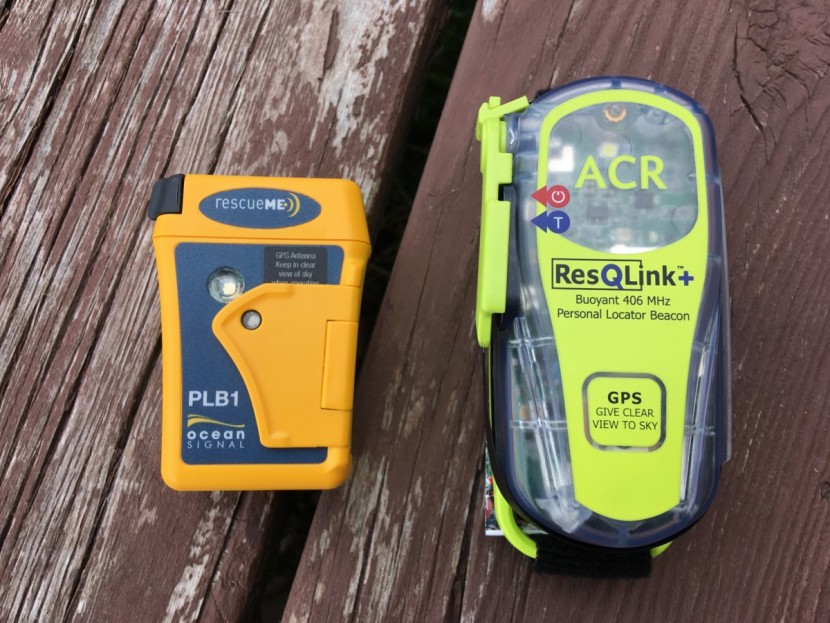
In our review, the Ocean Signal rescueME PLB1 and ACR ResQLink View use the COSPAS/SARSAT satellite and dispatch system and offer little more than SOS functionality. All products in our test provide some level of emergency messaging.
Non-Emergency Messaging
What if you want your loved ones to know that you are OK? The lack of an SOS message should reassure your emergency contacts in civilization ("no news is good news"), but it isn't definitive. If something really, really bad happens, you may be unable to activate the SOS mode on your device. If this uncertainty is overly stressful to your loved ones, having the option to send an “I'm OK” message is of value — even better if that “I'm OK” message contains information about your location. Because the COSPAS/SARSAT network is for emergency use only (with rare, unique, virtually unheard of exceptions), equipment leveraging that technology is unsuited for sending “OK” messages. Any device that sends an “OK message” must use a different civilian network.
Tracking
Tracking is essentially an automated “OK message” sent after initial activation, without your participation, and on some predetermined interval. Tracking data is sent to contacts you identify or to a web interface you can share in various ways. Loved ones at home sometimes enjoy “watching” your progress. Satellite messenger live tracking is fast becoming a standard way of verifying speed records and “fastest known times.” Not all satellite messaging services and products offer live tracking. OK messages and tracking don't give any customized or qualitative information about your progress or status.
Two-Way Messaging
What if you want to send more nuanced information from the wild? “Body and minds are all well, but this flooding creek will delay our exit a day. Don't worry about us in the meantime”. The preprogrammed “OK” message devices and systems make this sort of targeted information impossible. A device with no more advanced functionality can send a message like this is currently theoretical. If you want to communicate this way, you need to look for two-way communication options.
In most cases, two-way communications are very helpful. This is now what most regular users expect as standard. Two-way messaging is accessible and affordable enough that we recommend you seek it out. For instance, requesting certain types of field weather and conditions information is of great value. Regular, casual communication is very nice for maintaining all sorts of social and business relationships. Most shoppers will now consider only devices and services with two way custom messaging.
Coverage
There are two major questions you must be asking. We just discussed the main one. What sort of communications do you want and require? After that, the remaining consideration is coverage.
Communication Networks
There are a few different communication networks you must understand in order to understand your non-emergency messaging options. All of them can also transmit SOS messaging.
Public — COSPAS/SARSAT is the moniker for a global network of satellites explicitly configured for Search and Rescue communication and positioning. Devices made to access the COSPAS/SARSAT network do three things with the push of one button. Generally, these devices have just this one button to push, and just this one purpose to execute. Activating the SOS button of a COSPAS/SARSAT system PLB (Personal Locator Beacon is a phrase usually used to identify COSPAS/SARSAT devices):
- First ascertains location with regular GPS triangulation.
- Then sends that location, as well as your identifying information from the device and tied to your registration, to the COSPAS/SARSAT satellite network.
- Finally, the device transmits a distress signal on a different frequency that can be received and position-located by aircraft.
Depending on your location and the country you registered your COSPAS/SARSAT PLB with, the emergency satellite message and associated location and identification information are transmitted through one of a few national Search and Rescue (SAR) dispatch organizations. That SAR dispatch organization (in the United States it is a subdivision of our national weather service, with cooperation from both the Air Force and the Coast Guard) then works to secure the most local and most effective SAR resources. The required PLB registration, emergency dispatch protocol, and resource acquisition that accompanies a COSPAS/SARSAT activation is a tax-payer-supported “free” service like municipal fire or law enforcement services. With COSPAS/SARSAT, both the communication network and the dispatch service are public services provided by the government.
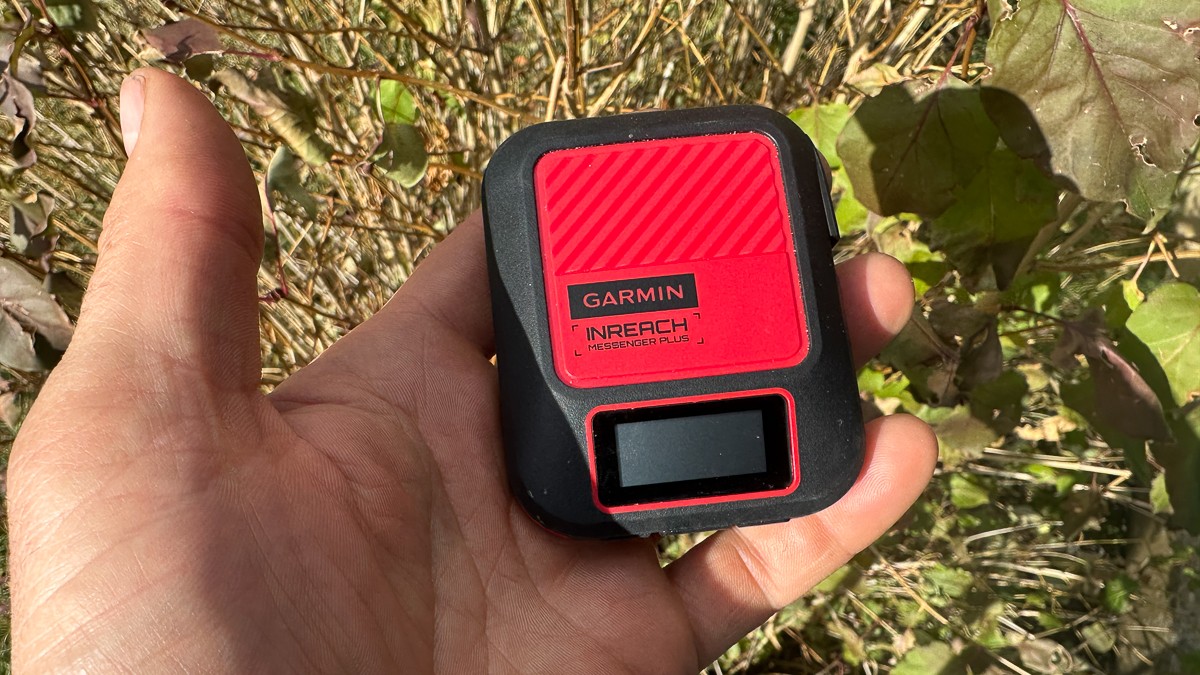
Private — The next type of emergency messaging is found in the private sector. Subscription-based devices and services employ one of a few commercial satellite communication networks and third-party dispatch services to simulate the COSPAS/SARSAT response. With these devices, adequately configured and subscribed, the user pushes an SOS button, and the device ascertains location with GPS signal and sends the info to a satellite and onto the ground. To this point, functionality is the same as on the COSPAS/SARSAT system. Devices using private-sector satellite networks do not transmit the secondary aeronautical distress signal. There are three major private-sector satellite networks. SPOT Devices and iPhone 14 use the Globalstar system of satellites (which is wide-ranging but not global), while Garmin, Somewear, and Bivy use the global Iridium satellite network.
The emergency message, with location and identity information embedded therein, is sent through a corporate dispatch office and on to local SAR resources. Device and service companies, without exception, contract out the monitoring and dispatch services. All private sector SOS messaging services (from Garmin, SPOT, Somewear, ZOLEO, and Bivy devices) contract one of three different private enterprises to handle monitoring and dispatch. Whether your SOS message is sent from a SPOT Gen4, Somewear Global Hotspot, or one of the other mentioned devices, it will funnel through GEOS, Garmin Response Team, Global Rescue, or Focus Point International. It will then be a dispatcher at that private enterprise that makes a phone call to a local SAR team.
In other parts of the world and other sectors, there are even more communication networks, dispatchers, and protocols. These are just the main players in the United States.
Because of the currently limited selection, communication type and signal coverage are tied together. However, there are exceptions. Essentially, you have the choice of global satellite coverage or regional satellite coverage. For truly worldwide coverage, COSPAS/SARSAT and the Iridium network are the only viable options. Globalstar, employed by SPOT devices and iPhone 14, is one we would consider to be “regional.” It is entirely possible that the Globalstar network will cover everywhere you might travel.
Most personal locator beacons or satellite communicators are equipped to clip to the outside of your backpack or clothing, which suggests that they should be. We don't recommend this. While GPS navigators are often clipped outside your pack because they work best when they have a clear view of the sky, your SOS device shouldn't necessarily be on at all times. You can feel comfortable turning it off and stowing it safely away, which lowers your chance of losing it. If you are tracking with your satellite device, it will work just fine inside the top of your backpack. We've tested all the tracking devices from inside our backpacks (always at or near the top) and have found little to no difference in tracking/messaging function.
Further, don't stress about it taking a little longer to dig the device out of your pack. The fact is, an emergency response will take hours at best. A few seconds to take your backpack off won't make any appreciable difference in the response time. Perhaps in those minutes, you will take a breath and realize that you don't actually need outside help. And worse than a few minutes of delay is losing your satellite communicator entirely. In summary, we don't recommend carrying these devices on the outside of your backpackSmartphone integrated Satellite Texting
Products from large cellular device manufacturers (Google, Apple, etc) now include satellite connectivity. The service and technology integration is new, but far more widespread than the outdoor-specific stand-alone devices. To include a satellite antenna in a smartphone requires that that antenna be very small. Connectivity, therefore, as compared to dedicated devices, is moodier, at best. In the case of the iPhone satellite messaging, the user must aim and hold the phone in a certain orientation for sending and receiving messages. For short and casual communications, this is totally acceptable. Especially, for now, as the service is essentially a free perk of your iPhone purchase. As promotional, free offers expire, the field will shake up again. For now, with free satellite services, the iPhone option is appealing and worthwhile.
Service Plans and Subscriptions
All communication equipment that we tested needs to be registered somehow. Some are free, while some present piles and piles of paid options. These options will be ever-changing and complicated to compare. There is a chart comparing various subscription options in our full satellite communicator review. We update that chart regularly, but details likely change even more frequently.
Conclusion
In your shopping, you will discover that devices sometimes come with more features than mentioned above. Notably, since SOS response requires GPS data, the devices include GPS antennae. With the hardware already there, manufacturers have taken steps to add navigational features to some products. With battery power precious, smartphone navigation being super accurate, and simplicity paramount in emergencies, we encourage you to think very critically before you rely a great deal on the navigational features of your communication device. At GearLab, we value multi-functionality. However, communication devices are somewhere we might draw the line. Our advice is to keep it simple. We don't count on navigating with our satellite communication devices and don't think you should either.